Relevant paper: [J1].
It is well recognized that stragglers, i.e., machines that perform considerably slower than average on a cluster, are a major bottleneck of distributed algorithms. In these cases, the result depends on local computations carried out by all servers; hence, the execution may be delayed if one of them is experiencing performance issues. In order to motivate this problem, we refer to Figure 1, which reports the average time to compute the product of two 2000x2000 matrices on 16 AWS EC2 t2.micro servers. Even though all machines have, in theory, the same specifications, we can see that two of them demonstrate straggling behavior, and their execution time has a large standard deviation.
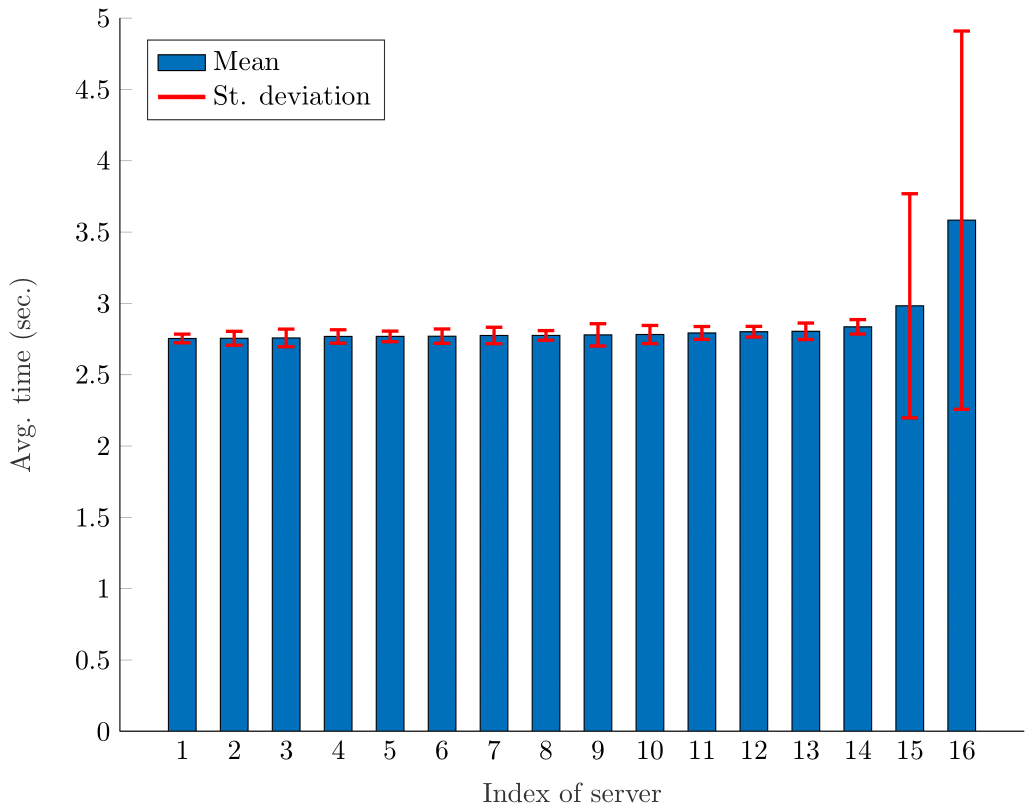 Figure 1: Mean and st. deviation of computation time of 16 AWS EC2 t2.micro machines.
Figure 1: Mean and st. deviation of computation time of 16 AWS EC2 t2.micro machines.
Recent work has demonstrated that straggler mitigation can be viewed as a problem in designing erasure codes. In a distributed matrix multiplication setup, the technique essentially maps the computation into the multiplication of smaller (coded) submatrices. The stragglers are treated as erasures in this process. The computation can be completed as long as a certain number of workers (called the recovery threshold) complete their assigned tasks. We have proposed a novel coding strategy for this problem when the absolute values of the matrix entries are sufficiently small. One of the main benefits that our approach enjoys is that the threshold has been significantly reduced compared to prior methods.
Next, we refer to Figure 2. A master node initially generates random input matrices A and B of size 8000x8000 with elements in the set {0, 1,…, 50}. These matrices remained the same for all experiments. Computation latency refers to the elapsed time from the point when all workers have received their inputs until enough of them finish their computations accounting for the decoding time. For this experiment, our algorithm can tolerate up to 6 stragglers while the prior one is resilient to up to 2 stragglers. We observe that when S reaches the corresponding value for each scheme, the computation latency jumps, and the entire algorithm is significantly delayed by the slowest server.
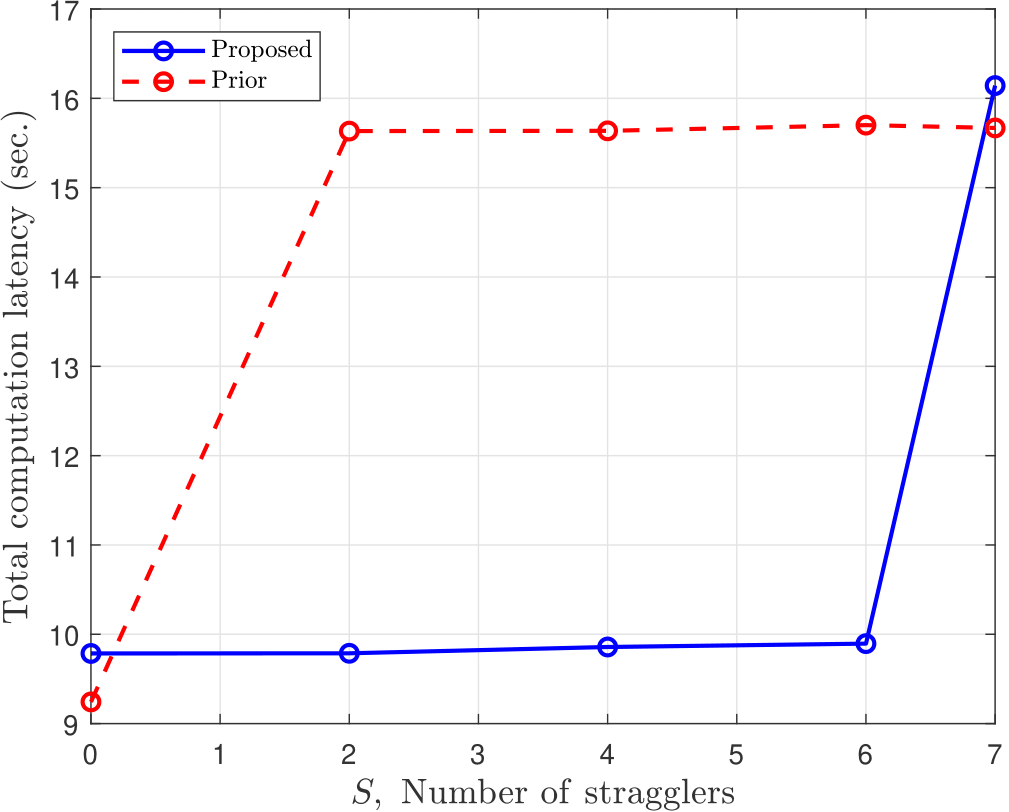 Figure 2: Comparison of total computation latency by simulating up to 8 stragglers.
Figure 2: Comparison of total computation latency by simulating up to 8 stragglers.
